Human coronavirus OC43 nucleoprotein C-terminal domain from S. cerevisiae, frozen
Description: Human coronavirus OC43 recombinant Nucleoprotein (OC43-rN) with deletion of N-terminal domain (OC43-ΔN-rN) expressed in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The construct contains amino acids 328-448 of the Nucleoprotein provided in UniProtKB sequence, accession number P33469 (NCAP_CVHOC), expressed with C-terminal His6-tag. It was purified from yeast lysates under native (non-denaturing) conditions using convenient chromatographic techniques. Then it was dialyzed against PBS, adjusted to 1.0 mg/ml concentration, filter-sterilized, aliquoted and frozen for storage.
Form: Frozen liquid in PBS (pH 7.4) with 500 mM NaCl.
Safety: Product 21-OC43delNN-ScB-F contains only yeast expressed proteins that are not infectious or hazard. Contains no plasma or serum of animal origin. No safety precautions are required.
Storage: The product is shipped with dry ice (shipment cost to Europe: 160 €). Store at -80°C for the long term. After thawing may be stored for short-term at 4°C (stable at least 1 week at this temperature). Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Concentration: 1.0 mg/ml.
Image: SDS-PAGE showing OC43-ΔN-rN product 21-OC43delNN-ScB-F at approximately 18 kDa (3 μg/lane).
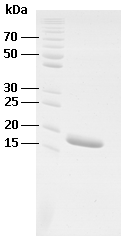
Purity: >95% pure OC43-ΔN-rN protein, as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Applications: ELISA, other immunoassays, Western blot, SDS-PAGE.
Note: Such truncated OC43-ΔN-rN protein construct without N-terminal domain has been reported to avoid cross-reactivity with other coronavirus nucleoproteins and improve specificity in serological assays compared to the full-length N protein (Ref. 1).
Unit/Price:
| Size | Catalogue No. | Price | |
| 100 μg | 21-OC43delNN-ScB-F-C | 200 € | Inquiry / Order product |
| 500 μg | 21-OC43delNN-ScB-F-D | 666 € | |
| 1 mg | 21-OC43delNN-ScB-F-M | 1000 € |
References:
- Edridge AWD, Kaczorowska J, Hoste ACR, Bakker M, Klein M, Loens K, Jebbink MF, Matser A, Kinsella CM, Rueda P, Ieven M, Goossens H, Prins M, Sastre P, Deijs M, van der Hoek L: Seasonal coronavirus protective immunity is short-lasting. Nat Med. 2020 Nov; 26(11):1691-1693. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1083-1.